Using medical monitors with materials that haven’t been rigorously tested against international safety standards is like walking a tightrope without a net. In environments like operating rooms or ICUs, a seemingly minor material flaw—poor flame retardancy or toxic emissions—can escalate into a critical safety event, endangering patients and staff. Imagine the fallout from equipment failing safety audits or, worse, causing harm. It’s a risk no healthcare professional or manufacturer should ever take.
Medical monitor materials must meet a stringent suite of international safety standards, including the IEC 60601 series for electrical safety and EMC, ISO 10993 for biocompatibility, RoHS and REACH for hazardous substance restrictions, and specific fire safety ratings like UL94. These ensure the materials are non-toxic, flame-retardant, corrosion-resistant, and safe for close patient and operator contact, crucial for global market acceptance and patient safety.

As specialists in medical display manufacturing, we at Reshin understand that navigating these complex standards is paramount. Let’s delve into why these regulations are critical and what they entail for the materials used in the devices you rely on daily.
Why Must Medical Monitor Materials Comply with International Safety Standards?
In high-stakes medical environments, equipment failure due to substandard materials isn’t just an inconvenience; it’s a direct threat. Monitors in ORs or ICUs can become ignition sources or harbor pathogens if not made correctly.
Compliance is non-negotiable because medical displays operate in high-risk areas like operating theatres and ICUs. Materials must possess flame retardant, anti-bacterial, and corrosion-resistant properties to prevent the equipment from becoming a safety hazard.
Medical displays are integral to modern healthcare, often positioned close to patients and medical staff for extended periods, especially in critical settings like operating theatres and intensive care units. My time in surgical imaging systems development has repeatedly shown me that the materials these devices are made from are not a trivial detail. If a monitor’s casing isn’t sufficiently flame-retardant1, an electrical fault could lead to a fire. If its surfaces aren’t resistant to harsh disinfectants, they can degrade, potentially harboring bacteria or leading to material failure. For instance, the constant cleaning can cause micro-cracks in inferior plastics, creating breeding grounds for pathogens. Furthermore, materials that off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs)2 can affect air quality and potentially the health of those in the vicinity. Therefore, ensuring materials have inherent safety features – flame retardancy, resistance to microbial growth3, and resilience against corrosion from cleaning agents – is essential. Otherwise, the very equipment designed to aid healing can become a potential hidden danger. This is a core principle guiding our material selection for all Reshin monitors.
Which International Standards Apply to the Material Selection of Medical Monitors?
Navigating the web of global regulations can seem daunting. Manufacturers can’t just pick any material; they must ensure it meets specific, internationally recognized safety benchmarks for medical electrical equipment.
The IEC 60601 series, particularly IEC 60601-1 (general safety) and IEC 60601-1-2 (EMC), are pivotal. These dictate material requirements for insulation, thermal stability, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, ensuring overall device safety.
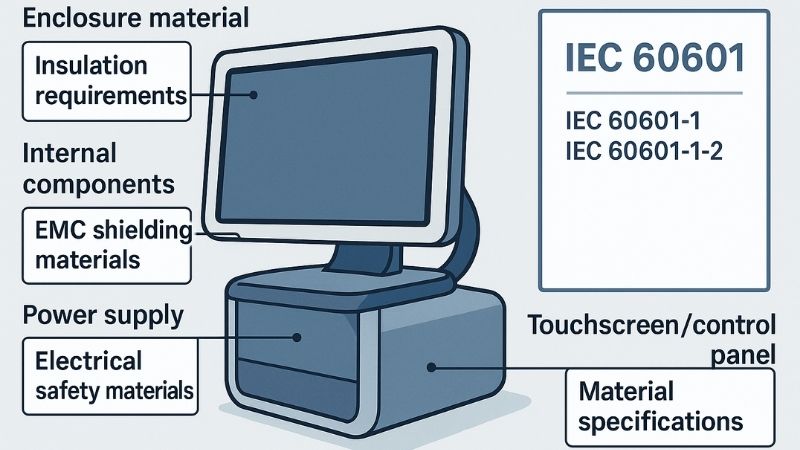
When we talk about the core standards governing medical electrical equipment, the IEC 60601 series4 is paramount. Specifically, IEC 60601-1 lays down the general requirements for basic safety and essential performance, and IEC 60601-1-2 addresses electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)5. These aren’t just suggestions; they are often legal requirements for market access in many regions, including for CE marking in Europe or FDA clearance in the US.
For materials, these standards have significant implications. For example, IEC 60601-1 dictates requirements for insulation materials to prevent electrical shock, demanding specific creepage and clearance distances which are influenced by the material’s comparative tracking index (CTI)6. It also covers thermal stability; materials must not deform or degrade under operational temperatures to a point where safety is compromised. Furthermore, enclosure materials must provide adequate mechanical strength and protection. The EMC standard, IEC 60601-1-2, ensures that the monitor doesn’t emit excessive electromagnetic interference that could affect other critical devices, and that it’s immune to interference from its environment. Material choices, such as conductive coatings or specific types of shielding within the monitor casing like those in our Reshin MS321PB, play a role here. Dr. Amy Chen, with her background in integrating OR equipment, would be acutely aware of how crucial EMC compliance is for harmonious system operation.
Fireproof, Non-toxic, Corrosion-resistant: What Performance Levels Are Required?
It’s not enough for materials to just ‘be there’. They must actively contribute to safety by resisting fire, not leaching toxins, and withstanding the harsh chemical environment of a hospital.
Materials must achieve specific performance levels, such as UL94 V-0 for fire retardancy and compliance with RoHS/REACH directives to restrict hazardous substances, ensuring they are non-toxic, fire-safe, and durable against corrosion.

Beyond the broad electrical safety covered by IEC 60601, specific material properties are critical. For fire safety, the UL94 standard is a key reference for flammability testing of plastic materials used in device enclosures. Medical display housings, especially for devices used in patient-critical areas, are typically required to meet the UL94 V-0 rating7. This means that if the material catches fire from an external source, it must self-extinguish within a very short time (seconds) and not drip flaming particles that could spread the fire. This is a vital safety feature.
For toxicity, regulations like the EU’s RoHS8 (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) directives are globally influential. RoHS restricts the use of specific hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and certain phthalates and brominated flame retardants in electrical and electronic equipment. REACH has a broader scope, addressing the production and use of chemical substances and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Compliance ensures that monitors, like our Reshin MS270P, do not pose a chemical threat to patients or healthcare workers through contact or off-gassing. Corrosion resistance is also key; materials must withstand repeated cleaning with hospital-grade disinfectants without degrading or corroding, maintaining both structural integrity and hygiene.
What Biocompatibility Requirements Apply to Medical Plastics and Metal Housings?
Since medical monitors are often in close proximity to patients, and sometimes even in direct contact, the materials they are made of must not cause adverse biological reactions. This is a fundamental safety concern.
Materials in patient-contact or patient-vicinity devices, like monitor housings, must comply with biocompatibility standards such as ISO 10993. This ensures they are non-cytotoxic, non-irritating, and non-sensitizing, preventing adverse reactions.

When a medical device, or parts of it, may come into direct or indirect contact with a patient’s body, biocompatibility becomes a critical consideration. The ISO 10993 series of standards, "Biological evaluation of medical devices," provides a framework for determining the appropriate biocompatibility testing9 for materials. For medical monitor housings and components that staff might touch and then touch patients, or that are in the immediate patient environment, ensuring these materials do not elicit a harmful biological response is essential.
Tests under ISO 1099310 can include assessing cytotoxicity (whether the material is toxic to cells), sensitization (whether it can cause an allergic reaction after repeated exposure), and irritation (whether it can cause inflammation or irritation on contact). While a monitor casing might not be an "implant," parts of it are frequently touched, and it resides within the patient’s environment, especially in an OR or ICU. Therefore, demonstrating that the plastics (like medical-grade ABS11 or polycarbonate) and metal alloys (like medical-grade aluminum) used in products such as our Reshin MS275P or MS430PC do not leach harmful substances or cause skin reactions is a key part of the overall safety assessment. This ensures that the device itself doesn’t contribute to patient complications.
How Does Reshin Ensure Its Materials Meet Global Medical Certifications?
Claims of compliance are easy to make, but rigorous testing and a commitment to quality processes are what truly ensure materials meet stringent global medical certifications, protecting both patients and your institution’s reputation.
Reshin meticulously selects medical-grade materials, subjects them to rigorous biocompatibility (ISO 10993) and safety testing, and ensures all OR-grade products, like the MS275P, comply with global certification systems.
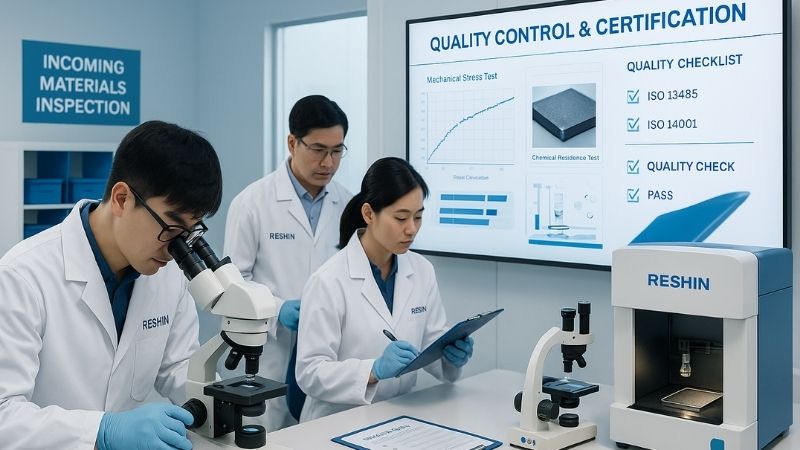

At Reshin, ensuring our materials meet and exceed global medical certifications12 is not an afterthought; it’s integrated into our design and manufacturing DNA. Our commitment starts with the careful selection of raw materials. We partner with reputable suppliers who can provide comprehensive documentation and test reports for their medical-grade plastics, alloys, and coatings. Our R&D team, with over 200 members each boasting more than a decade of experience, is deeply familiar with standards like IEC 60601, ISO 10993, RoHS, and REACH.
For all our products intended for critical environments, such as the MS275P (27" 4K Surgical Monitor) and the larger MS430PC (43" 4K Surgical Monitor), we conduct rigorous internal testing and also engage third-party accredited laboratories for independent verification. This includes checks for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, flammability (e.g., UL94 V-0 for enclosures), hazardous substance content, and biocompatibility13 where appropriate. This thorough approach is why global brands like Philips and Fujifilm trust Reshin for their OEM/ODM needs and why our displays are used in over 100,000 hospitals worldwide. It’s how we ensure safety and reliability under intensive use, providing peace of mind to users like Dr. Amy Chen who demand precise, reliable, and, above all, safe imaging systems.
Conclusion
Adherence to international safety standards for medical monitor materials is not just a regulatory hurdle but a fundamental commitment to patient and user safety, ensuring reliability and trust in critical healthcare settings worldwide.
-
Explore the importance of flame-retardant materials in medical displays to ensure safety and prevent fire hazards in healthcare settings. ↩
-
Learn about the impact of VOCs on air quality in healthcare, crucial for patient and staff safety in medical facilities. ↩
-
Discover why materials resistant to microbial growth are vital for maintaining hygiene and preventing infections in medical devices. ↩
-
Understanding the IEC 60601 series is essential for compliance in medical equipment, ensuring safety and performance standards are met. ↩
-
Exploring EMC in medical devices reveals how it ensures safe operation and prevents interference, crucial for patient safety. ↩
-
Learning about CTI helps in selecting safe insulation materials, vital for preventing electrical shocks in medical equipment. ↩
-
Understanding the UL94 V-0 rating is crucial for ensuring fire safety in medical devices, especially in patient-critical areas. ↩
-
Exploring the EU’s RoHS regulations helps ensure medical devices are safe from hazardous substances, protecting patients and workers. ↩
-
Learn about various biocompatibility testing methods to ensure medical devices are safe for patient use. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the ISO 10993 standards, which are crucial for ensuring medical device safety and biocompatibility. ↩
-
Discover the properties and applications of medical-grade ABS in medical devices, ensuring safety and compliance. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the importance of medical certifications in ensuring product safety and compliance in healthcare. ↩
-
Discover the significance of biocompatibility in medical devices to ensure they are safe for patient use and minimize adverse reactions. ↩



