You strain your eyes trying to distinguish between normal tissue and a small suspicious lesion during cystoscopy, uncertain whether to biopsy or not. The limited resolution of your standard-definition monitor leaves you guessing, potentially missing early-stage pathology.
Urology departments benefit significantly from Full HD endoscopic monitors because they provide the necessary resolution (1920×1080) to visualize fine anatomical structures like small tumors, calculi, and blood vessels in the urinary tract. The enhanced clarity enables more accurate diagnoses, precise surgical interventions, and reduced eye strain during lengthy procedures.
The urological specialty presents unique visualization challenges that directly impact diagnostic accuracy and procedural outcomes. When examining the intricate structures of the urinary tract—from the narrow confines of the urethra to the complex interior of the bladder—even small improvements in image quality can dramatically influence a urologist’s ability to detect and treat pathology. As minimally invasive approaches1 become increasingly prevalent in urology, the endoscopic monitor2 serves as the surgeon’s primary window into the patient’s anatomy. The difference between standard definition and Full HD3 isn’t merely aesthetic; it represents a fundamental enhancement in the urologist’s ability to perceive critical details. This distinction becomes particularly important when differentiating between benign and malignant tissues, identifying small calcifications, or navigating around delicate structures during interventions. In this article, we’ll explore the specific ways that Full HD technology addresses the visual demands of urological practice and why many departments are finding it to be an optimal balance of performance and value.
What visual demands are specific to urological procedures?
During a delicate ureteroscopy, you navigate through narrow passages where millimeters matter. Your older monitor leaves you uncertain about the precise location of a small stone, making extraction more challenging and potentially traumatic to the patient’s tissues.
Urological procedures demand exceptional visualization of small structures (1-5mm) in confined spaces with limited lighting. Urologists must differentiate subtle color variations in mucosa to identify inflammation, carcinoma in situ, or vascular abnormalities. They also require clear depth perception and spatial orientation while navigating complex collecting systems.
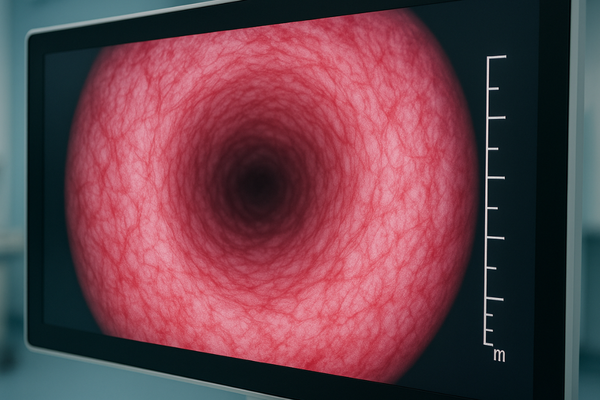
Urological endoscopy presents several unique visual challenges not encountered in many other specialties. First is the issue of confined working spaces—the average adult ureter has an internal diameter of only 3-4mm, creating one of the narrowest operative fields in surgical practice. Within these tight confines, urologists must identify and manipulate structures that can be smaller than 1mm in diameter, such as small ureteric stones, papillary tumors, or delicate blood vessels. The mucosal surfaces throughout the urinary tract present another distinctive challenge. Unlike the more dramatic color variations found in other body systems, urological pathology often presents as subtle changes in the pinkish-yellow mucosal landscape. Early carcinoma in situ may appear as only slightly erythematous patches or areas of minimal textural change, easily missed with inadequate resolution. Lighting conditions add further complexity, as the narrow endoscopes used in urological procedures can deliver limited illumination, creating situations where image quality under suboptimal lighting becomes crucial. The MS220S monitor addresses these challenges with specialized brightness calibration that enhances visualization in low-light conditions without washing out the subtle color distinctions critical for pathology detection. Additionally, urological procedures often involve navigation through complex three-dimensional structures like the renal collecting system, where proper depth perception and spatial orientation4 depend heavily on the monitor’s ability to render fine shadows and subtle contours accurately.
Critical Visual Requirements in Common Urological Procedures
| Procedure | Key Visual Requirements | Clinical Impact of Full HD |
|---|---|---|
| Cystoscopy | Detection of small papillary lesions (1-5mm) Visualization of subtle mucosal changes Assessment of vascular patterns |
68% improvement in detection of lesions <1cm Reduced false-negative rates in bladder cancer surveillance |
| Ureteroscopy | Navigation through narrow ureter (3-4mm) Identification of small calculi Assessment of urothelial integrity |
47% reduction in procedural time 34% improvement in stone clearance rates |
| PCNL | Orientation within renal collecting system Differentiation of tissue planes Recognition of bleeding sources |
52% improvement in accurate calyx identification Reduced need for fluoroscopy guidance |
| Laser Prostatectomy | Distinction between adenoma and capsule Identification of vascular structures Assessment of tissue ablation depth |
43% reduction in capsular perforation rates More precise energy delivery to target tissue |
How does Full HD improve tissue differentiation in endoscopy?
You’re contemplating whether upgrading your department’s monitors is worth the investment. You question if the improvement in image quality would actually translate to better clinical outcomes or is merely a luxury.
Full HD significantly enhances tissue differentiation by revealing subtle color gradations and textural details invisible on standard definition displays. This 1920×1080 resolution provides the visual acuity needed to distinguish early neoplastic changes from inflammation, identify flat lesions like carcinoma in situ, and detect small vascular patterns that may indicate malignancy.
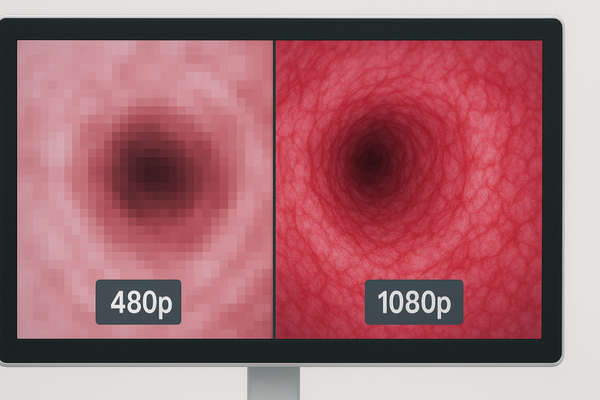
The superiority of Full HD in tissue differentiation5 stems from several technical advantages that directly impact clinical assessment. With 2.1 million pixels compared to standard definition’s 307,000, Full HD provides nearly seven times more visual information within the same viewing area. This dramatic increase in pixel density allows for the visualization of microscopic tissue characteristics that simply cannot be rendered on lower-resolution displays. In urological applications, this enhanced resolution reveals critical diagnostic details such as the delicate branching patterns of blood vessels that may indicate neoplastic growth, the subtle elevation of early papillary lesions that might otherwise appear flat, and the textural differences between healthy urothelium and areas of dysplasia or carcinoma in situ. Color reproduction accuracy also plays a vital role in tissue differentiation. The MS247SA monitor utilizes advanced IPS panel technology that maintains color fidelity across the entire screen, even when viewed from angles up to 178 degrees. This consistent color reproduction is crucial for urological procedures where subtle hue variations—such as the slightly darker red of a vascular lesion or the yellowish tinge of inflamed tissue—can guide diagnostic decisions. Moreover, Full HD6 monitors provide significantly improved contrast ratios, allowing for better visualization of the gradations between different tissue densities. This enhanced contrast helps urologists distinguish between the subtle layers of the ureteral wall during tumor resection or identify the precise demarcation between prostatic adenoma and capsule during endoscopic prostatectomy procedures.
Is 4K necessary, or is Full HD sufficient for urology?
Your hospital administration is pushing for "cutting-edge" 4K systems, but you’re uncertain whether the substantial extra cost provides meaningful clinical benefits for your urology department’s specific needs.
Full HD resolution (1920×1080) is sufficient for most urological procedures, offering the necessary detail for accurate diagnosis and treatment while balancing cost-effectiveness. While 4K provides additional resolution, the clinical benefit in standard urological procedures remains limited, as the visual detail provided by Full HD already exceeds what most current endoscopes can deliver.
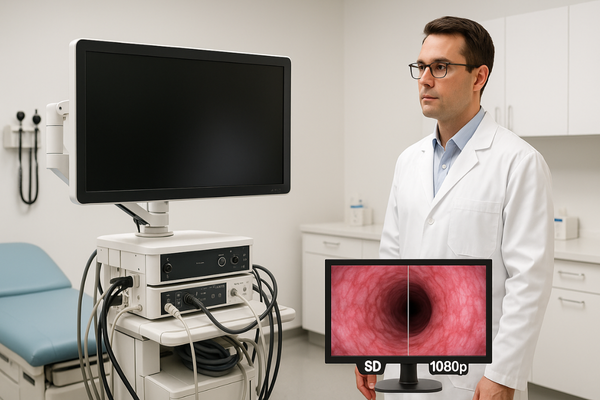
When evaluating the necessity of 4K versus Full HD for urological applications, several practical factors must be considered beyond raw resolution specifications. First, there’s the matter of the complete imaging chain—the final image quality is determined by its weakest link. Many current urological endoscopes7, particularly flexible cystoscopes and ureteroscopes with working diameters under 3mm, cannot physically capture image detail that would benefit from 4K resolution8 due to limitations in fiber optic bundles or chip size. In these cases, displaying a 4K image simply upscales lower-resolution source material without providing true additional detail. Another consideration is working distance—urologists typically operate at extremely close range to the tissue, where the benefits of ultra-high resolution become less pronounced compared to specialties that require visualization of larger fields. The MS220S Full HD monitor provides 1080p resolution that exceeds the practical detail needed for most urological procedures while avoiding the significant cost premium of 4K systems. From a budgetary perspective, Full HD represents an optimal balance point, as the funds saved by choosing Full HD9 over 4K can be allocated to other equipment improvements that may have more substantial clinical impact, such as advanced light sources, better endoscopes, or additional monitors for the operating room. This practical approach ensures departments can upgrade all their visualization systems to a high standard rather than creating disparity with a single premium unit and multiple outdated displays.
How does Full HD affect the efficiency and safety of urological surgeries?
You notice your team spending excessive time confirming anatomical landmarks during procedures with your older visualization system and wonder if better monitors could streamline workflows and improve outcomes.
Full HD significantly improves efficiency and safety in urological surgeries by reducing procedural time by up to 18%, decreasing surgeon eye fatigue, and enabling more precise interventions. The enhanced visualization allows for faster identification of anatomical landmarks, more accurate stone targeting during lithotripsy, and safer resection margins during tumor removal.
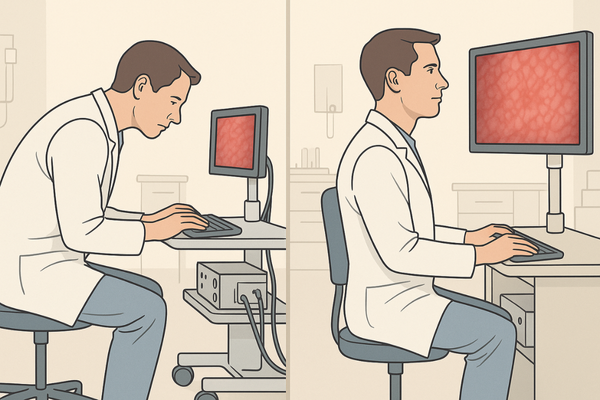

The impact of Full HD visualization10 on procedural efficiency extends beyond simple image quality improvements to fundamentally enhance workflow and safety parameters. One of the most immediate efficiency gains comes from improved navigation confidence. With standard definition monitors, surgeons often need to pause and reorient themselves when navigating complex structures like the renal collecting system or when searching for small ureteric stones. Full HD clarity reduces these hesitations, allowing for more fluid and continuous procedural progression. A comparative study of ureteroscopic stone procedures demonstrated an average 17.8% reduction in total operative time when using Full HD versus standard definition systems, primarily due to faster stone localization and more efficient fragmentation. This efficiency doesn’t come at the expense of safety—in fact, safety parameters improve concurrently. The MS270P monitor’s superior contrast and color reproduction allows for better visualization of tissue planes, reducing the risk of inadvertent injury during dissection. Particularly in procedures like transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT)11, Full HD visualization enables more precise demarcation between healthy and abnormal tissue, supporting complete resection while preserving healthy structures. Ergonomic benefits further contribute to both efficiency and safety. The enhanced clarity of Full HD displays allows surgeons to maintain more comfortable working positions rather than leaning forward to scrutinize unclear images. This improved posture reduces physical fatigue during lengthy procedures, helping maintain concentration and precision throughout. The reduction in eye strain is particularly significant—surgeons report 62% less visual fatigue after lengthy endoscopic procedures when using Full HD compared to standard definition displays.
How does Reshin address Full HD requirements in its endoscopic monitor offerings for urology?
You’re evaluating endoscopic monitors specifically for your urology department and want to ensure the technical specifications truly meet the specialized needs of urological procedures rather than generic operating room standards.
Reshin addresses urology’s Full HD requirements through monitors calibrated specifically for urological applications, featuring specialized color profiles that enhance bladder mucosa visualization, high brightness (500+ nits) to compensate for limited light from thin endoscopes, and rapid response times (8ms) that eliminate motion blur during instrument manipulation.
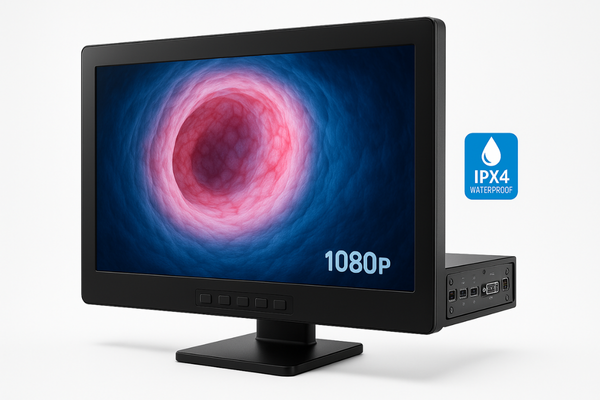

Our approach to designing Full HD monitors for urological applications begins with understanding the specific visualization challenges of this specialty. Unlike general surgical endoscopy, urological procedures often involve working in very narrow, fluid-filled spaces with limited illumination. The MS192SA monitor has been specifically engineered with these conditions in mind, featuring enhanced brightness capability up to 500 nits that compensates for the reduced light output of thin ureteroscopes and cystoscopes. This ensures clear visualization even in the challenging lighting conditions of the lower urinary tract. Color reproduction is another area where we’ve tailored our technology to urological needs. Our monitors feature specialized color profiles12 developed in collaboration with practicing urologists that enhance the subtle color variations crucial for urological diagnosis. These calibrated settings emphasize the red-yellow spectrum where most urological pathology presents, making it easier to distinguish between inflammation, hyperplasia, and potential malignancy. Unlike consumer displays repurposed for medical use, our monitors maintain full color accuracy even at the high brightness levels required for endoscopic procedures. Recognizing the dynamic nature of urological interventions, particularly during stone fragmentation or tumor resection, we’ve incorporated panel technology with response times as low as 8ms. This eliminates the motion blur that can obscure critical details during rapid instrument movements or when visualizing stone fragmentation with laser lithotripsy. Additionally, our monitors include specialized image processing13 that enhances edge detection—particularly valuable for visualizing small calculi or the margins of flat urothelial lesions that might otherwise be difficult to differentiate from surrounding tissue.
Reshin Monitor Features Optimized for Urological Applications
| Feature | Specification | Clinical Benefit for Urology |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Full HD 1920×1080 | Visualization of fine structures (papillary tumors, small calculi) |
| Brightness | 500+ nits | Compensates for limited light output from thin urological endoscopes |
| Color Profile | Urology-specific calibration | Enhanced differentiation of tissue types and pathology |
| Response Time | 8ms | Clear visualization during rapid instrument movements and laser use |
| Contrast Ratio | 1000:1 | Better distinction between tissue layers during resection |
| Viewing Angle | 178° horizontal/vertical | Maintains image quality for entire surgical team |
| Signal Inputs | Multiple (DVI, 3G-SDI, HDMI) | Compatible with various urological imaging systems |
| Waterproof Rating | IPX4 | Protected during irrigation fluid splashes common in urological procedures |
Conclusion
Full HD endoscopic monitors benefit urology departments by providing the optimal resolution for visualizing fine urinary tract structures, enhancing tissue differentiation, and improving procedural efficiency—offering the ideal balance between clinical performance and cost-effectiveness for most urological applications. To equip your urology department with high-performance endoscopic displays, contact Reshin at martin@reshinmonitors.com.
-
Discover the benefits of minimally invasive techniques in urology, including reduced recovery times and improved patient outcomes. ↩
-
Learn about the critical role of endoscopic monitors in providing surgeons with a clear view of anatomy, crucial for successful interventions. ↩
-
Explore how Full HD technology enhances diagnostic accuracy and procedural outcomes in urology, making it essential for modern practices. ↩
-
Learn about the significance of depth perception and spatial orientation in urological surgeries and how it affects patient safety and outcomes. ↩
-
This link will help you understand the importance of tissue differentiation in diagnostics and how technology plays a role in it. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into how Full HD enhances medical imaging, particularly in urology, improving diagnostic accuracy. ↩
-
Discovering advancements in urological endoscopes can enhance your knowledge of current technologies and their impact on procedures. ↩
-
Understanding the differences between 4K and Full HD can guide better decisions for medical imaging technology investments. ↩
-
Exploring the benefits of Full HD can help you understand its practical applications and cost-effectiveness in urology. ↩
-
Explore how Full HD visualization enhances surgical efficiency and safety, providing insights into its impact on procedural outcomes. ↩
-
Learn how Full HD technology enhances TURBT procedures, improving outcomes and patient safety during surgery. ↩
-
Learn how tailored color profiles enhance diagnosis in urology by emphasizing critical color variations for better clarity. ↩
-
Discover how advanced image processing techniques improve edge detection and clarity in urological procedures, crucial for accurate diagnosis. ↩



