Bright ambient light often obscures crucial details on medical displays. This can compromise diagnostic accuracy. Anti-glare coatings improve visibility, but do they impact color precision?
Yes, anti-glare coatings can slightly affect color fidelity. The degree of impact depends on the coating’s type and quality. High-quality, multi-layer coatings are designed to minimize color shifts, thereby preserving the accuracy vital for medical imaging.
Anti-glare technology is essential for modern medical displays. This article explores the role of these coatings, how different types influence color, their effect on calibration, and how manufacturers achieve a balance. We will also discuss our approach to optimizing these treatments.
What is the purpose of anti-glare coating in medical displays?
Glare on display screens can be a significant distraction. This reduces visibility during critical medical procedures. Anti-glare coatings are designed to counteract this specific problem effectively.
The primary purpose of anti-glare coatings in medical displays is to reduce reflections from ambient light sources. This enhances screen visibility and readability, particularly in brightly lit environments like operating rooms or diagnostic settings.
In medical environments, especially operating rooms and intensive care units, bright overhead lighting is common. This light can reflect off display surfaces, creating glare. Glare obscures vital patient information, strains the eyes of medical staff, and can lead to misinterpretations. Anti-glare coatings1 work by scattering or absorbing this reflected light. This diffusion makes the screen content clearer and easier to read from various angles. Improved readability reduces visual fatigue2 for practitioners during long procedures. This ultimately supports better patient outcomes3 by ensuring information is always clearly visible.
How do different types of anti-glare coatings influence color accuracy?
Not all anti-glare solutions offer the same performance. Some types can inadvertently degrade image quality. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for medical professionals selecting displays.
Different anti-glare coatings influence color accuracy in varying ways. Etched surfaces might diffuse light more, potentially causing slight image softness or minor color desaturation. High-quality multi-layer anti-reflection (AR) coatings generally maintain better color accuracy and contrast.
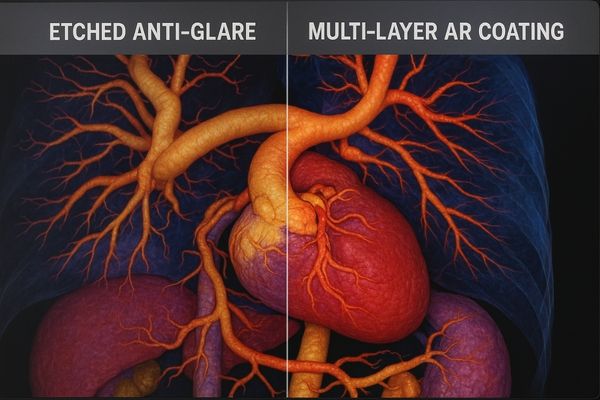
The two main types of anti-glare treatments are etched surfaces and multi-layer coatings.
Etched Anti-Glare
Etched anti-glare surfaces create a microscopic texture on the display’s outer layer. This texture scatters ambient light, reducing specular reflections. While effective at minimizing glare, this scattering can sometimes slightly diffuse the light emitted from the display itself. This may lead to a minor reduction in sharpness or a subtle desaturation of colors. The effect is often minimal but can be a concern for applications requiring utmost color precision.
Multi-Layer Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
Multi-layer AR coatings work on the principle of optical interference. Thin layers of materials with different refractive indices are applied to the screen. These layers cause reflected light waves to interfere destructively, canceling each other out. This significantly reduces reflections without substantially scattering the emitted light. As a result, AR coatings tend to preserve color fidelity4, contrast, and sharpness more effectively than some etched surfaces. High-transmittance AR materials are key to this.
| Coating Type | Glare Reduction | Color Fidelity | Sharpness Preservation | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etched Surface | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Lower |
| Multi-Layer AR | Excellent | High | High | Higher |
This table shows that while etched surfaces are cost-effective, multi-layer AR coatings typically offer superior performance in preserving image quality.
Can anti-glare layers distort grayscale or DICOM calibration?
Accurate representation of grayscale images is fundamental for many medical diagnoses. Concerns about coatings affecting this critical aspect of display performance are certainly valid.
High-quality anti-glare layers, particularly well-engineered AR coatings, generally do not distort grayscale perception or DICOM calibration significantly. The calibration process itself can account for the minor, consistent optical properties of a high-clarity coating.
The DICOM Part 14 Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF)5 ensures perceptual linearity in medical images. This means that changes in pixel values correspond to just noticeable differences (JNDs) in brightness for the human eye. Anti-glare coatings introduce an additional optical layer. If this layer is not uniform or has poor optical quality, it could theoretically interfere. However, reputable medical display manufacturers use high-clarity coatings with consistent optical properties. Calibration systems, which measure luminance directly from the display surface, can compensate for the slight, uniform attenuation or diffusion caused by a quality anti-glare layer. The key is that the coating’s impact must be consistent across the entire screen surface. As long as the coating maintains high clarity and uniformity, it typically does not impede accurate grayscale reproduction or diagnostic precision.
How do manufacturers balance glare control and color fidelity?
Reducing distracting screen glare is highly important for usability. Yet, maintaining precise color accuracy is absolutely paramount for diagnostic confidence. Manufacturers face a complex technical challenge to achieve both goals.
Manufacturers balance glare control and color fidelity by employing advanced optical designs. This frequently involves sophisticated multi-layer anti-reflection (AR) coatings that minimize reflections while maximizing light transmission, thereby preserving color purity and contrast.
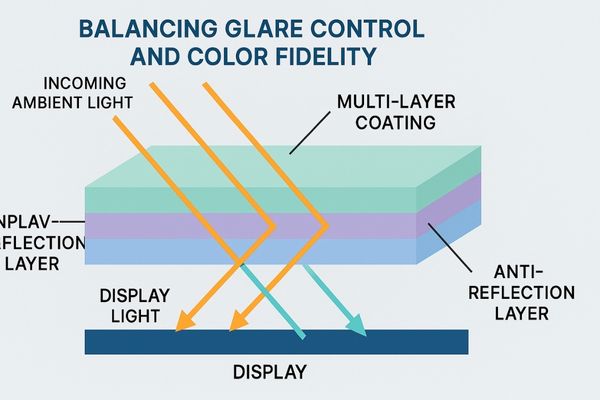
The challenge lies in reducing unwanted external reflections without negatively affecting the light emitted from the display’s pixels. Simple diffusion techniques can reduce glare but may also scatter the display’s own light, leading to reduced sharpness and color saturation. To overcome this, manufacturers invest in advanced coating technologies6. Multi-layer AR coatings7 are a prime example. These consist of several microscopically thin layers of different optical materials. Each layer is precisely engineered to manipulate light waves through interference. This process cancels out reflected light across a broad spectrum of wavelengths while allowing the display’s light to pass through with minimal disruption. The selection of materials and the precision of their application are critical. This ensures high light transmittance8, maintaining image brightness, contrast, and color integrity.
| Coating Property | Impact on Glare | Impact on Color Fidelity | Desired State for Medical Displays |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Reflectivity | Direct | Indirect (via contrast) | As low as possible |
| Light Transmittance | None | Direct | As high as possible |
| Haze Level | Indirect | Can affect | Low, but balanced with diffusion |
| Coating Uniformity | Minor | Can affect if poor | High |
This table outlines key properties manufacturers manage to achieve an optimal balance.
How does Reshin optimize anti-glare treatment without sacrificing color quality?
Medical professionals may find it difficult to select displays that offer excellent glare reduction. They also need displays that do not compromise on critical color accuracy. Our approach focuses on achieving this precise balance.
We optimize anti-glare treatment by employing advanced multi-layer anti-reflection (AR) coatings. These are often combined with anti-smudge properties. This ensures minimal reflectivity while maintaining high color accuracy, targeting standards like sRGB or BT.709 for our displays.

Our commitment is to deliver superior image quality in all viewing conditions. We achieve this by carefully selecting and applying specialized coatings to our medical displays, such as those in our MS series surgical monitors. Our process involves using multi-layer AR coatings9 designed to reduce surface reflections to very low levels. Simultaneously, these coatings are engineered for high light transmission, ensuring that the original color and brightness of the image are preserved. We also incorporate anti-smudge layers10. These make the displays easier to clean and maintain optical clarity. This combination results in displays that offer excellent readability under bright ambient lighting, such as in operating rooms, without sacrificing the color precision needed for high-resolution surgical imaging. Our target is to achieve near-100% coverage of color spaces like sRGB or BT.70911, ensuring true-to-life image reproduction.
Conclusion
Anti-glare coatings are vital for medical displays, enhancing visibility. While some types can slightly affect color, advanced multi-layer AR coatings effectively balance glare reduction with high color fidelity. For medical displays with optimized anti-reflective coating technology, contact Reshin at martin@reshinmonitors.com.
-
Explore how anti-glare coatings enhance visibility and reduce eye strain in critical medical settings, improving patient care. ↩
-
Learn about the impact of visual fatigue on healthcare workers and how to mitigate it for better performance and patient safety. ↩
-
Discover the key elements that contribute to improved patient outcomes in ICUs, including technology and staff well-being. ↩
-
Learning about color fidelity is crucial for anyone interested in high-quality visual displays and accurate color representation. ↩
-
Understanding GSDF is crucial for ensuring accurate medical imaging and diagnostic precision. Explore this link to learn more about its significance. ↩
-
Exploring advanced coating technologies reveals how manufacturers improve display performance and user experience. ↩
-
Understanding Multi-layer AR coatings can enhance your knowledge of display technology and its impact on image quality. ↩
-
Learning about light transmittance helps you appreciate the factors that affect display brightness and color accuracy. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how multi-layer AR coatings enhance image quality and reduce reflections, crucial for medical displays. ↩
-
Learn about anti-smudge layers and their role in maintaining optical clarity and ease of cleaning for medical displays. ↩
-
Discover the significance of color spaces like sRGB and BT.709 in achieving true-to-life image reproduction in medical displays. ↩



