Endoscopic surgery demands extremely clear visuals for success. Choosing a monitor with inadequate resolution can compromise delicate maneuvers. This guide will help you understand how to select the optimal display resolution.
To choose the right resolution, select a 4K UHD (3840×2160) monitor for most endoscopic procedures. This offers an excellent balance of detailed clarity for precise tasks and manageable data processing. Consider your specific surgical needs and existing camera system compatibility.
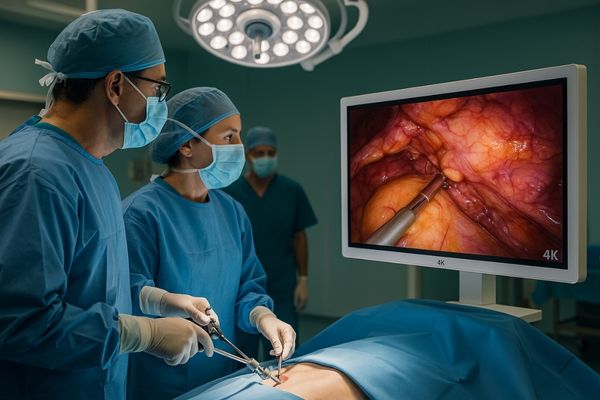
The quality of the image a surgeon sees is paramount in modern minimally invasive surgery. The resolution of the surgical display plays a central role in providing that critical visual information. We will explore why resolution is so important, the common levels available, its impact on surgical tasks, potential trade-offs, and suitable monitor options for endoscopy. This will help you make an informed decision.
Why is resolution critical in endoscopic surgery?
Surgeons perform intricate tasks under significant pressure. Poor image detail during endoscopy can obscure vital structures. This can directly affect the safety and effectiveness of the procedure.
Resolution is critical in endoscopic surgery because it directly determines the visibility of fine anatomical details. Clearer, higher-resolution images enable surgeons to identify subtle tissue changes, distinguish delicate structures, and perform precise actions like dissection or suturing with greater confidence.
Endoscopic surgery1 is fundamentally reliant on visual guidance. The surgeon navigates and operates within the body by viewing images transmitted from a small camera at the tip of the endoscope. Higher resolution2 translates to more pixels on the screen, which means more information is displayed. This increased pixel density allows for the visualization of much finer details. For instance, surgeons can more easily distinguish between different tissue layers, identify tiny blood vessels that need to be coagulated or avoided, and precisely manipulate instruments for tasks like suturing or removing pathological tissue. Enhanced detail visibility3 not only improves the accuracy of these maneuvers but also helps in recognizing anatomical variations or unexpected findings. Ultimately, superior image clarity contributes to reduced procedure times, minimized risk of complications, and better patient outcomes. It allows for a more confident and efficient surgical workflow.
What resolution levels are commonly used in endoscopic monitors?
The market offers many surgical displays with various resolution specifications. This range of options can sometimes make it difficult to choose. We will now explain the most common resolution levels you will encounter for endoscopic applications.
Commonly used resolution levels for endoscopic monitors include Full HD (1920×1080 pixels, approximately 2MP) and 4K UHD (3840×2160 pixels, approximately 8.3MP). While 8MP native displays also exist, 4K UHD is increasingly the standard, offering a significant clarity improvement over Full HD.
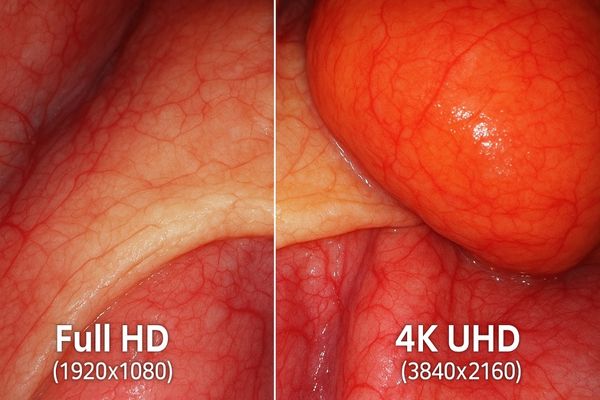
The resolution of a display refers to the number of distinct pixels it can show in each dimension.
Full HD (FHD)4
Full HD resolution, which is 1920 pixels horizontally by 1080 pixels vertically, provides about 2.1 million pixels in total. For many years, FHD was the standard for endoscopic imaging. It offers a decent level of detail for many routine procedures. However, as camera technology has advanced, FHD can now be a limiting factor for visualizing the finest structures.
4K Ultra HD (UHD)5
4K UHD resolution significantly increases the pixel count to 3840 x 2160, totaling approximately 8.3 million pixels. This is four times the number of pixels found in Full HD. This substantial increase in pixel density results in a dramatically sharper and more detailed image. For endoscopy, 4K UHD allows surgeons to see much finer nuances in tissues and enhances their ability to perform complex tasks. It is widely considered a "sweet spot" because it offers exceptional clarity without overly taxing image processing systems in most modern setups. Our MS430PC is an example of a display that brings this 4K UHD clarity to the operating room.
Higher Resolutions (e.g., 8MP)6
True 8MP resolution monitors (which might refer to displays with slightly more pixels than 4K UHD or specific sensor-pixel matching) are also becoming available. These are typically used in specialized applications or on very large screens where the additional detail can be appreciated. The key is to match the monitor resolution to the capabilities of the endoscopic camera system to gain the full benefit.
| Resolution Name | Pixels (Width x Height) | Total Pixels (Approx.) | Typical Endoscopic Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full HD (FHD) | 1920 x 1080 | 2.1 million | Basic procedures, older camera systems |
| 4K UHD | 3840 x 2160 | 8.3 million | Standard for modern, detailed endoscopy |
| 8MP (and above) | e.g., 4096 x 2160+ | 8.8 million+ | Advanced procedures, large screen formats |
This table summarizes common resolutions and their typical applications in endoscopy.
How does higher resolution impact surgical precision and depth perception?
Surgeons require more than just a sharp, two-dimensional image on screen. A lack of perceived depth or subtle detail can make intricate tasks more challenging. We will explore how higher resolution enhances not only clarity but also spatial awareness.
Higher resolution greatly improves surgical precision by rendering finer anatomical details, crucial for accurate dissection and tissue identification. It also enhances depth perception cues, especially with 3D endoscopic systems, aiding in better spatial orientation and instrument manipulation.
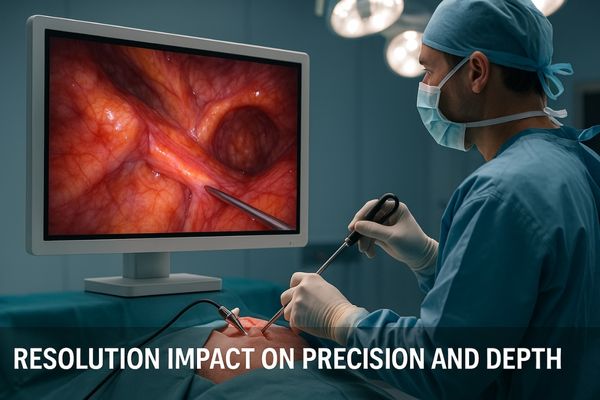
The impact of higher resolution on surgical precision7 is direct and significant. With more pixels displaying the surgical site, surgeons can better differentiate between tissue planes, identify minute nerves and blood vessels, and assess subtle changes in tissue texture or color that might indicate pathology. This level of detail is crucial for precise dissection, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue, and ensuring complete removal of diseased areas. For example, during a complex laparoscopic procedure, clearly seeing the margin between a tumor and normal tissue allows for a more accurate resection.
Beyond sharpness, higher resolution8 also contributes to improved depth perception. Even in 2D imaging, the increased detail in textures, shadows, and highlights provides more cues for the brain to interpret depth. This effect is even more pronounced in 3D endoscopic systems9. When each eye receives a high-resolution image, the stereoscopic effect is enhanced, leading to a more natural and accurate perception of three-dimensional space. This improved spatial awareness allows surgeons to judge distances more accurately and manipulate instruments with greater confidence, particularly when working in confined spaces or performing delicate suturing. The ability to overlay anatomical references or visual aids from other imaging modalities also benefits greatly from higher underlying display resolution, ensuring these augmented reality elements are sharp and correctly aligned.
Is there a trade-off between resolution and image processing latency?
The prospect of an ultra-high-resolution image in surgery is very attractive. However, processing more data can sometimes introduce an unwelcome delay, or lag, in the displayed image. We will now look at the crucial balance between image clarity and real-time responsiveness.
Yes, a trade-off can exist between resolution and image processing latency. Higher resolutions mean more data must be processed per frame, potentially increasing display lag if the system’s image processor or signal pathway is not adequately optimized. Therefore, low-latency design in surgical monitors is essential.
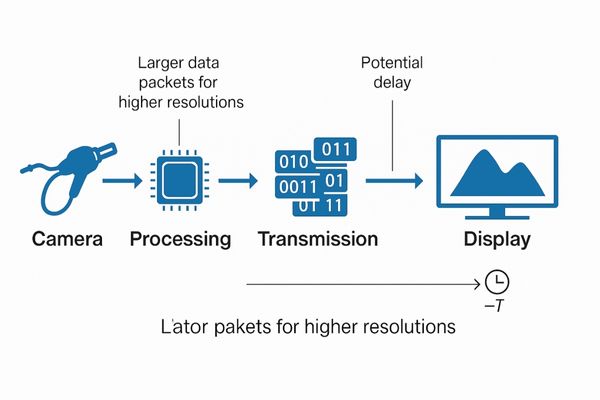
Image latency refers to the delay between the moment the endoscopic camera captures an image and the moment it appears on the surgical display. In surgery, even a small delay can be disorienting and can affect hand-eye coordination. Higher resolution images contain significantly more data than lower resolution ones. For example, a 4K UHD image10 has four times the pixel data of a Full HD image. Processing this increased amount of data in real-time—performing tasks like scaling, color correction, and enhancement—requires substantial processing power within the display and a high-bandwidth connection (like HDMI 2.0 or DisplayPort 1.2 and above) from the video source.
If the display’s internal electronics or the video signal chain cannot handle this data load efficiently, latency can increase. This means the surgeon might see a slight delay between their hand movements and the corresponding action on the screen. This can lead to misjudging instrument positions, slower and more hesitant movements, and increased surgeon fatigue. In severe cases, image tearing or stuttering might also occur if the display cannot keep up with the incoming video signal. Therefore, it is critical that surgical monitors, especially those with 4K or higher resolutions, are specifically engineered for low latency11. This involves using powerful image processors, optimized firmware, and high-speed signal interfaces. Displays like our MS275P are designed with these considerations to minimize latency for critical surgical applications.
Which Reshin monitor models are best suited for endoscopic applications?
Finding the perfect monitor that meets all the demanding requirements of endoscopic surgery can seem like a complex task. You need a display that not only provides exceptional image quality but also integrates seamlessly into the operating room environment. We will introduce our monitor solutions specifically optimized for endoscopic clarity and performance.
Our MS275P (27-inch) and MS430PC (43-inch) series surgical monitors are excellently suited for endoscopic applications. They deliver 4K UHD resolution for superior detail, feature rapid image response times, and incorporate DICOM Part 14 compliance, making them ideal for various procedures including laparoscopy and urology.
We have developed specific monitor series tailored to the unique demands of endoscopic surgery. The MS275P (a 27-inch model) and the MS430PC (a 43-inch model) are prime examples. Both series feature 4K UHD (3840×2160) resolution12, providing the exceptional image clarity and detail essential for modern minimally invasive procedures. This high resolution allows surgeons to visualize fine anatomical structures with greater precision.
Beyond resolution, these monitors are designed for fast response times. This minimizes motion blur during rapid camera movements, ensuring a consistently clear view. They also support DICOM Part 14 grayscale calibration13. While endoscopy is primarily color imaging, this feature is valuable if surgeons need to simultaneously view reference images like X-rays or CT scans on the same display, ensuring accurate grayscale representation.
Furthermore, these models offer excellent color accuracy and a wide color gamut, which ensures that the colors of tissues and organs are rendered faithfully, aiding in identification and assessment. Additional surgical-specific features include anti-glare surfaces14 to reduce reflections from bright OR lights, sealed front panels for easy cleaning and disinfection, and a variety of input options to connect to different endoscopic camera systems. These features make them highly suitable for a range of endoscopic procedures, such as laparoscopy, arthroscopy, hysteroscopy, and urological surgeries, providing surgeons with the visual tools they need for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct resolution, ideally 4K UHD, is vital for modern endoscopic surgery. This enhances image detail, improves precision, and supports better patient outcomes. Our monitors offer solutions designed for these demanding applications. To explore 4K UHD displays optimized for endoscopic use, contact Reshin at martin@reshinmonitors.com.
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into the advantages and advancements in endoscopic surgery, enhancing your understanding of its impact on patient care. ↩
-
This link will help you understand the significance of image resolution in surgery, showcasing its role in enhancing precision and safety during operations. ↩
-
Discover how enhanced detail visibility can transform surgical practices, leading to better outcomes and fewer complications for patients. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the importance of Full HD in imaging and its applications in various fields. ↩
-
Discover how 4K UHD enhances medical imaging and improves surgical precision, making it a game-changer in healthcare. ↩
-
Learn about the advantages of higher resolution displays in endoscopy and how they can improve diagnostic capabilities. ↩
-
Learn about the advancements in imaging technologies that significantly boost surgical precision and patient safety. ↩
-
Explore how higher resolution enhances surgical precision and outcomes, making it essential for modern surgical practices. ↩
-
Discover the unique benefits of 3D endoscopic systems in enhancing surgical techniques and outcomes. ↩
-
Exploring the advantages of 4K UHD images can enhance surgical precision and outcomes, making it a vital resource for medical professionals. ↩
-
Discovering the significance of low latency in surgical monitors can help in selecting the right equipment for optimal surgical performance. ↩
-
Explore how 4K UHD enhances medical imaging, providing clarity and detail crucial for surgical precision. ↩
-
Learn about DICOM Part 14 calibration and its role in ensuring accurate grayscale representation in medical imaging. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of anti-glare surfaces in surgical monitors for reducing reflections and enhancing visibility during procedures. ↩



