Standard displays compress image details in the brightest and darkest areas. This loss of information can compromise a diagnosis. High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology solves this problem.
HDR enhances medical imaging with a wider dynamic range, improved lesion visibility through better contrast, and more accurate tissue differentiation via a wide color gamut, benefiting both diagnostics and surgery.
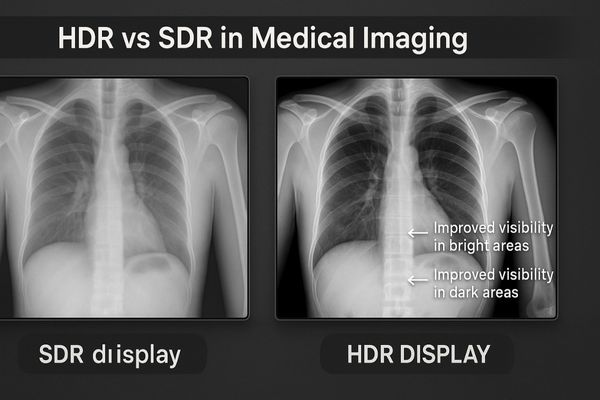
HDR is more than just a buzzword; it is a fundamental shift in how visual information is presented. Let us examine how this technology directly impacts clinical work.
HDR Expands Dynamic Range for Medical Imaging
Conventional medical images often hide details in shadows or bright spots. Clinicians may miss subtle cues hidden in these areas. HDR technology reveals this full spectrum of information.
HDR technology displays a much wider luminance range. This allows clinicians to see crucial details in both the very bright and very dark portions of a single image simultaneously.
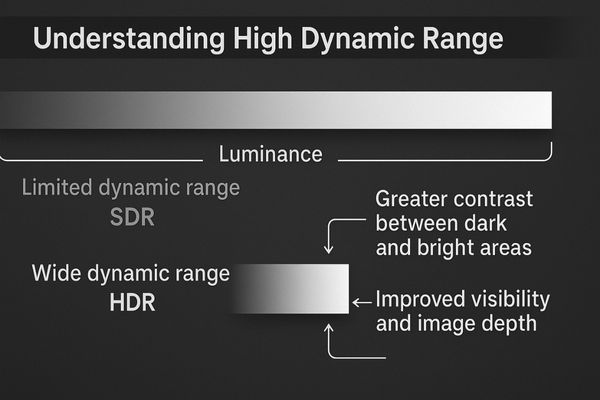
Dynamic range1 refers to the ratio between the brightest white and the darkest black a display can produce. Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) displays have a limited range, which forces them to compromise on image data. They either clip the details in bright areas, turning them into pure white, or crush details in dark areas, turning them into pure black. HDR technology2 overcomes this limitation. It utilizes a higher bit depth for color and brightness information and often employs advanced backlighting. This allows an HDR display to render a scene with specular highlights and deep, detailed shadows in the same frame. For modalities that capture a wide range of tissue densities, like CT scans or digital radiography, this is transformative. Clinicians can clearly see subtle structures within dense bone and adjacent soft tissue without constantly adjusting window and level settings. This capability improves diagnostic efficiency and reduces the risk of missing critical information. The MD51CHY – 34" 5MP Diagnostic Monitor for X-ray Imaging is engineered to provide the wide canvas and detail needed for such comprehensive radiological review.
Enhanced Contrast Improves Lesion Visibility
Subtle lesions can blend into surrounding tissue on a standard screen. This lack of contrast makes early detection difficult and uncertain. HDR technology makes these abnormalities stand out clearly.
By significantly boosting local contrast, HDR helps radiologists and clinicians detect subtle lesions, microcalcifications, or vascular anomalies. This capability directly enhances diagnostic confidence and accuracy.
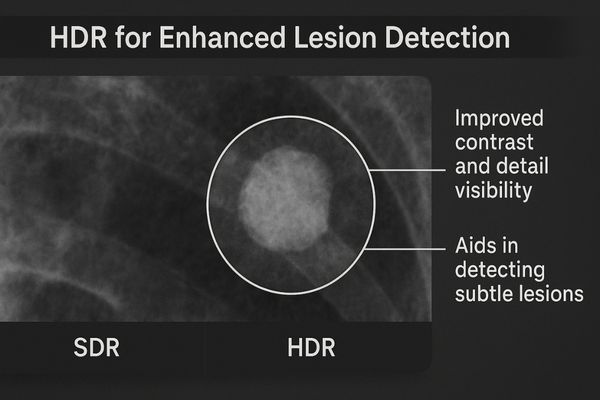
Contrast is the visual difference that separates objects from one another. HDR improves contrast in a more sophisticated way than simply increasing the overall brightness. It uses metadata embedded in the video signal to manage luminance on a local, pixel-by-pixel basis. This means it can make a tiny, bright calcification significantly brighter than the surrounding tissue, which might be in a much darker part of the image. This technique, known as local dimming3, creates a greater sense of depth and realism, making it easier for the human eye to perceive fine details. In angiography, this enhanced contrast4 can help define the edges of a narrowed blood vessel with greater precision. For radiologists reviewing a CT scan, it helps to better delineate the borders of a tumor from healthy organs. This improved separation of structures reduces ambiguity, leading to faster and more confident diagnostic decisions. The large panel of the MD46C – Dual-screen Diagnostic Monitor (Single Panel) is ideal for leveraging HDR to compare current and prior studies, where subtle changes in lesion contrast are critical.
| Feature | Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) | High Dynamic Range (HDR) |
|---|---|---|
| Luminance | Limited range (~100-300 nits) | Expanded range (>1000 nits) |
| Contrast | Global adjustment, often flat | Localized, high contrast |
| Detail Visibility | Details lost in bright/dark areas | Details preserved across the range |
| Depth Perception | Flat, 2D appearance | Enhanced sense of depth |
Wide Color Gamut Supports Accurate Tissue Differentiation
Inaccurate color on a surgical monitor can make all tissue look similar. This makes it difficult to identify critical structures like vessels or nerves. HDR’s wide color gamut ensures precision.
HDR is often paired with a wide color gamut (WCG). This combination faithfully represents tissue colors, which is extremely valuable during endoscopy and surgery for distinguishing different tissue types.
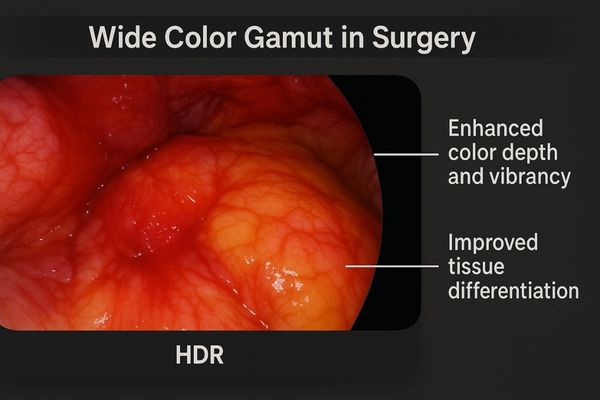
HDR technology is about more than just brightness and contrast; it is also about color. Most HDR standards are designed to work with a Wide Color Gamut (WCG)5. A color gamut defines the total range of colors a display can reproduce. Standard displays are typically limited to the sRGB color space, which covers only a fraction of the colors the human eye can see. HDR displays6 often support wider gamuts like DCI-P3, which can show more saturated and distinct shades of red, green, and blue. In the operating room, this makes a significant difference. During a laparoscopic procedure, the ability to see subtle variations in the redness of tissue can indicate blood perfusion or inflammation. The precise color of tissue helps the surgeon more accurately identify anatomical planes, differentiate a ureter from a vessel, and assess tissue viability. WCG provides the expanded palette of colors, while HDR provides a greater number of shades and brightness levels within that palette. The MS275P – 27" 4K Surgical Monitor, with its 4K resolution and advanced color capabilities, is built to leverage these technologies for superior surgical visualization.
HDR Benefits Multi-Modality and Surgical Applications
Combining images from different sources often results in a washed-out view. Important details are lost when fusing modalities like CT and PET. HDR maintains clarity for all combined signals.
HDR technology excels in multi-modality imaging fusion, such as PET-CT. It is also highly effective in endoscopic surgery, maintaining high-dynamic quality even when integrating multiple video signals.
The benefits of HDR are particularly evident in complex imaging scenarios. One key application is multi-modality image fusion7. This technique involves overlaying a functional scan, like a brightly colored PET scan, onto a grayscale anatomical scan, like a CT. On an SDR display, the intense colors of the PET data can cause the subtle grayscale details of the underlying CT to become washed out. HDR resolves this conflict. It allows the display to render the bright, saturated colors showing metabolic activity while simultaneously preserving the fine, low-contrast details of the anatomical structures. In surgery, the operating room display must often show several sources at once, such as the 4K endoscopic camera feed, patient vitals from a monitor, and a preoperative MRI scan. HDR technology8 ensures that each of these windows is displayed with optimal fidelity, reflecting the full dynamic range of its original source without compromise. The MS321PC – 32" 4K Surgical Monitor is designed for these multi-signal environments, providing the performance needed to manage complex visual data with clarity.
| Application | Key Benefit of HDR |
|---|---|
| Radiology (CT/MRI) | Visibility of detail in dense bone and soft tissue simultaneously. |
| Endoscopic Surgery | Accurate differentiation of tissue types through better color and depth. |
| Multi-Modality (PET-CT) | Prevents loss of detail when fusing bright color and grayscale images. |
| Angiography | Clearer delineation of vessel walls and vascular anomalies. |
Adoption Challenges Include Cost and Standardization
Hospitals want to adopt the best technology, but HDR seems expensive and complicated. The lack of a single, clear standard creates confusion and purchase hesitation. These factors are slowing adoption.
High initial costs and the lack of a unified HDR standard for medical imaging remain significant hurdles. But as the technology matures, its long-term clinical benefits are becoming increasingly clear.
Despite its clear clinical advantages, the widespread adoption of HDR in medicine faces two main obstacles. The first is cost. HDR displays9 require more advanced components, including powerful image processors and sophisticated backlight systems with local dimming capabilities. These elements increase the manufacturing cost, which results in a higher purchase price compared to SDR displays. The second challenge is the lack of standardization10. In the consumer market, several HDR formats compete (e.g., HDR10, Dolby Vision, HLG). The medical industry has not yet established a single, universal standard for how HDR information should be captured by modalities, stored and transmitted within the DICOM framework, and interpreted by displays. This creates potential interoperability problems. However, the push for HDR is strong. As manufacturing scales and costs decrease, and as industry bodies work toward a unified standard, these barriers will diminish. The clear clinical benefits are driving demand, ensuring HDR will become a key feature in future medical displays like the MS270P – 27" FHD Surgical Display, which provides a solid foundation for next-generation imaging.
Conclusion
HDR technology significantly improves medical imaging by revealing more detail. It enhances diagnostic confidence and surgical precision. Its adoption represents a major step forward for visual accuracy in healthcare.
📧 Want to leverage HDR technology in your clinical workflows? Contact Martin at martin@reshinmonitors.com to explore Reshin’s advanced medical display solutions.
-
Understanding dynamic range is crucial for appreciating how displays handle contrast and detail, enhancing your viewing experience. ↩
-
Exploring HDR technology reveals its benefits in delivering stunning visuals, making it essential for anyone interested in high-quality displays. ↩
-
Understanding local dimming can enhance your knowledge of HDR technology and its benefits in imaging. ↩
-
Exploring enhanced contrast will reveal its crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging. ↩
-
Understanding WCG is crucial for appreciating how HDR enhances color reproduction in displays, especially in medical settings. ↩
-
Exploring HDR displays will reveal their impact on visual quality, essential for fields like surgery where precision is vital. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how multi-modality image fusion enhances imaging techniques and improves diagnostic accuracy. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of HDR technology in medical imaging and how it enhances visual clarity and detail. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of HDR displays in medical settings, including improved image quality and clinical outcomes. ↩
-
Understanding the importance of standardization can help address interoperability issues and enhance HDR technology adoption. ↩



