Low-quality displays can obscure critical details in CT scans. This limitation can lead to missed findings and compromised patient care. Specialized medical displays provide the clarity needed for accurate diagnosis.
The value of a medical display in CT diagnosis lies in its ability to render complex imaging data with exceptional clarity and accuracy. It ensures radiologists can confidently identify subtle pathologies, directly improving diagnostic precision and patient outcomes.
Understanding these factors is critical for any healthcare institution. The quality of a diagnostic display1 directly influences a radiologist’s ability to interpret complex anatomical information. Let us explore the key elements that make medical displays2 indispensable for CT diagnosis.
Precision Imaging Requires High-Resolution Displays
CT scans are filled with immense detail. A standard monitor can blur these fine points. High-resolution displays are essential to see every critical element with absolute clarity.
CT imaging contains vast amounts of detail. High-resolution medical displays are critical for rendering the subtle anatomical structures and pathological changes captured in scans. This precision ensures radiologists can make confident and accurate diagnoses.
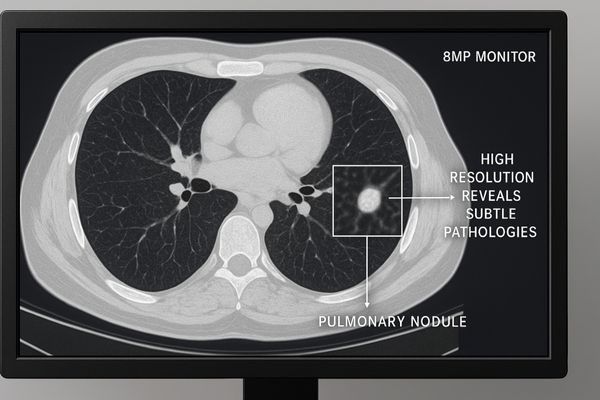
The value of high resolution goes beyond just a sharper picture. In CT imaging3, the data is captured in a large matrix, often 512×512 pixels or more, across hundreds of slices. To view this data without loss of information, the display must have enough pixels to render the image on a one-to-one basis. A lower-resolution screen forces the image to be downscaled, causing pixels to be averaged or discarded. This process can easily obscure fine textures, small nodules, or hairline fractures. For instance, identifying early-stage lung cancer requires spotting ground-glass opacities that are faint and small. A high-resolution display4 ensures these subtle patterns are distinct and measurable. Our MD85CA provides a large canvas with exceptional pixel density. This allows radiologists to view entire CT slices at their native resolution, eliminating the need for excessive panning and zooming that can disrupt workflow and lead to diagnostic fatigue. The clarity it provides is fundamental to confident
| Display Resolution | Pixel Count (Approx.) | Suitability for Detailed CT |
|---|---|---|
| Full HD (2MP) | 1920 x 1080 | Basic review, not ideal for primary diagnosis |
| QHD (4MP) | 2560 x 1440 | Good for general radiology |
| 4K UHD (8MP) | 3840 x 2160 | Excellent for primary CT diagnosis |
| 12MP | 4200 x 2800 | Ideal for multi-modality and mammography |
Grayscale Accuracy Enhances CT Lesion Detection
Not all shades of gray are the same. Inaccurate grayscale rendering can hide lesions in plain sight. Precise grayscale is vital for distinguishing between tissues of different densities.
Accurate grayscale representation is vital for differentiating tissues with slight density variations. This capability directly improves the detection rate of lesions in CT scans and increases the radiologist’s diagnostic confidence.
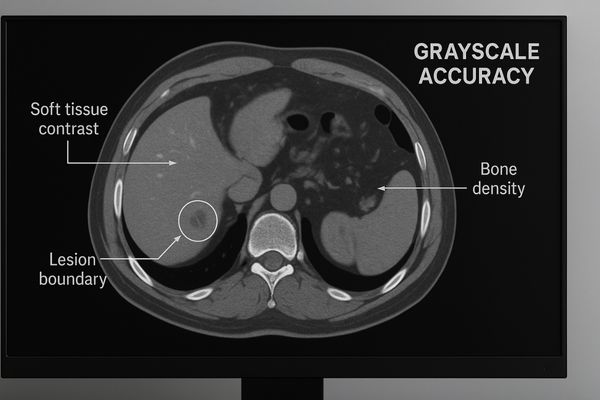
CT scanners measure the radiodensity of tissues and assign them a value on the Hounsfield scale5. These values are then translated into shades of gray on a display. The ability to distinguish between very similar gray tones is what allows a radiologist to differentiate healthy tissue from pathological tissue. For example, a liver metastasis may have a density only slightly different from the surrounding healthy liver parenchyma. A standard consumer display, with its limited bit depth and emphasis on vibrant colors, cannot reproduce these subtle grayscale variations accurately. It might lump multiple distinct shades into one, rendering the lesion invisible. A high-quality medical display6, however, is designed for this specific task. The MD33G – 3MP Grayscale Diagnostic Monitor, for instance, supports a higher bit depth, allowing it to display a greater number of simultaneous shades of gray. This ensures that the subtle differences in density captured by the CT scanner are faithfully reproduced on the screen, giving the radiologist the visual information needed to detect and characterize abnormalities with high confidence.
DICOM Calibration Ensures Reliable Diagnostic Quality
Images often look different on every screen. This inconsistency is a significant risk in medicine. DICOM calibration standardizes image appearance, ensuring diagnostic reliability across all calibrated displays.
DICOM calibration standardizes how CT images are displayed. This consistency across different monitors and facilities is crucial for reducing diagnostic errors caused by variations in image presentation.
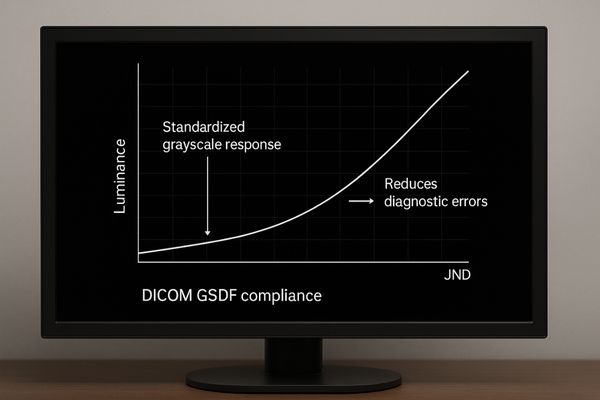
The DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standard is the backbone of modern medical imaging. Part 14 of this standard defines the Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF)7. This function dictates the precise luminance level a display must produce for each specific digital value in an image file. The goal is perceptual linearization, which means that changes in grayscale values appear consistent to the human eye across the entire grayscale range. Without adherence to DICOM GSDF, a display might show an image that is too dark, hiding details in the shadows, or too bright, washing out details in the highlights. This can lead to misinterpretations, especially when comparing a patient’s current scan to a prior one viewed on a different monitor. We embed DICOM compliance8 deep into our monitor designs. Models like the MD26GA – 2MP Diagnostic Monitor feature built-in calibration sensors that continuously check and adjust the display’s output to maintain perfect alignment with the DICOM curve. This guarantees that every clinician sees the image exactly as intended, providing a stable and reliable foundation for diagnosis.
| Feature | Uncalibrated Display | DICOM Calibrated Display |
|---|---|---|
| Image Consistency | Poor (Varies by device) | Excellent (Standardized) |
| Grayscale Rendition | Inaccurate | Perceptually Linear (GSDF) |
| Diagnostic Risk | High | Low |
| Clinician Trust | Low | High |
Brightness Uniformity Maintains Image Integrity
Your screen might have hidden dim spots. These dark patches can easily obscure vital information. True brightness uniformity across the entire display ensures every part of an image is clearly visible.
Poor brightness uniformity creates dimmer areas on a display. This can obscure subtle yet critical details within a CT scan, preventing radiologists from conducting a thorough and accurate analysis.

Brightness uniformity is a measure of how consistent the luminance is across the entire surface of the screen. In many consumer-grade displays, the center is significantly brighter than the corners and edges. If a subtle but critical finding, like a small hemorrhage or an early-stage tumor, happens to fall in one of these dimmer areas, it can be easily missed. This problem is particularly acute on larger displays, where maintaining even illumination from the backlight is an engineering challenge. To address this, we use advanced technology called Digital Uniformity Correction (DUC)9. During manufacturing, each display is measured at hundreds of points to map its unique brightness variations. This map is then used to create a correction profile stored in the monitor’s firmware. In real-time, the monitor adjusts the brightness of individual pixels to compensate for any inconsistencies, ensuring a perfectly uniform image from edge to edge. On our large-format displays like the MD46C – Dual-screen Diagnostic Monitor (Single Panel), this technology is essential. It provides a seamless, consistent viewing area that empowers radiologists to review large datasets with confidence, knowing that no detail is hidden by a flaw in the display.
Evolving Needs Drive Advances in CT Display Technology
Diagnostic needs are growing more complex every day. Yesterday’s technology simply cannot keep up. Display innovation is therefore essential to support the future of CT imaging.
The demands of modern diagnostics are pushing display technology forward. Innovations in AI, ultra-high resolutions, and multi-modality fusion are shaping the next generation of CT displays to meet these advanced needs.
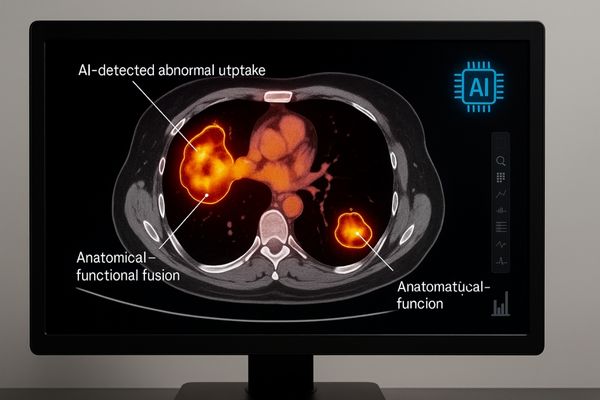
The field of radiology is rapidly evolving, and display technology must evolve with it. The rise of artificial intelligence in diagnostics10 is one major driver. AI algorithms can now analyze scans and highlight suspicious regions for the radiologist. Displays must be able to render these AI overlays clearly without obscuring the underlying anatomical detail. Another key trend is multi-modality image fusion11, such as combining the anatomical detail of CT with the functional information of PET scans. This requires displays that excel at rendering both precise grayscale and vibrant color images on the same screen. Furthermore, workflow efficiency is pushing the industry toward larger, seamless monitors that can replace traditional dual-monitor setups, reducing head and eye movement for the radiologist. Our most advanced monitors, like the MD120C – 12MP High-Precision Diagnostic Monitor with AI Calibration, are designed to meet these challenges. With its ultra-high resolution, hybrid gamma capabilities for both color and grayscale, and integrated AI-assisted tools, it provides a platform ready for the next generation of diagnostic imaging.
Conclusion
High-quality medical displays are not a luxury. They are a necessity for accurate CT diagnosis. Resolution, grayscale, calibration, and uniformity are the pillars supporting reliable interpretation and better patient outcomes. To secure high-performance displays for CT imaging, contact Reshin at martin@reshinmonitors.com.
-
Understanding the role of diagnostic displays can enhance the quality of medical imaging and improve patient outcomes. ↩
-
Exploring this topic reveals how advanced medical displays can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. ↩
-
Learn more about CT imaging to grasp its significance in modern medicine and how it aids in early disease detection. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how high-resolution displays enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve patient outcomes.
interpretation. ↩ -
Understanding the Hounsfield scale is crucial for interpreting CT scans accurately, enhancing diagnostic skills. ↩
-
Exploring the advantages of high-quality medical displays can improve diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. ↩
-
Understanding GSDF is crucial for ensuring accurate medical imaging and diagnosis, making this resource invaluable for professionals. ↩
-
Exploring DICOM compliance will enhance your knowledge of imaging standards, ensuring better diagnostic accuracy and patient care. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how DUC enhances display quality, crucial for accurate medical imaging. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how AI is transforming diagnostics and enhancing radiology practices. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of multi-modality image fusion and its impact on diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. ↩



