Connecting your 4K surgical camera but seeing only a low-resolution or unstable image can halt a procedure. This frustrating technical barrier prevents you from accessing critical visual information when it matters most.
Different video interfaces have distinct resolution limits based on their bandwidth. HDMI 2.0 supports 4K at 60Hz, while HDMI 2.1 handles 8K. DisplayPort 1.4 manages 4K at 144Hz or 8K with compression. SDI varies from HD to 4K depending on the standard (3G/6G/12G). DVI is limited to 2K, while USB-C/Thunderbolt can reach 4K or higher.
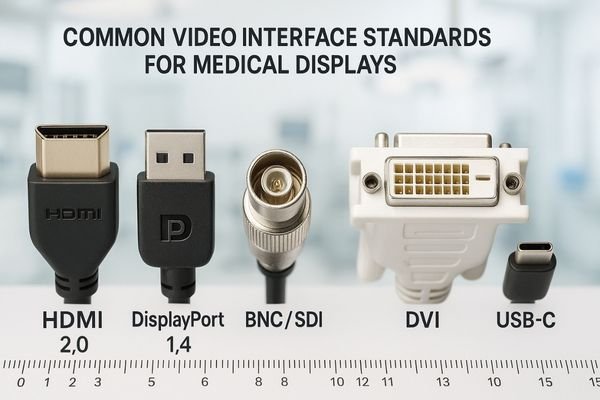
Modern operating rooms are increasingly dependent on high-resolution imaging1. The clarity and detail provided by 4K and higher resolutions2 allow for better identification of tissue structures, more precise instrument manipulation, and improved clinical outcomes. However, getting this high-resolution video from the camera to the display is not as simple as it might seem. The interface—the physical connection and its associated protocol—acts as a bottleneck that can restrict the resolution, color depth, and refresh rate. Choosing the wrong interface for your needs can result in compromised image quality or even complete incompatibility. This article will explore the capabilities and limitations of today’s most common video interfaces3, helping you understand which standards are best suited for various surgical imaging scenarios.
How does HDMI differ from DisplayPort in supporting 4K and 8K resolutions?
You need to display ultra-high-resolution surgical images without compression or lag. Will HDMI be enough, or should you invest in DisplayPort connections throughout your operating room?
HDMI 2.0 supports 4K at 60Hz with 8-bit color, while HDMI 2.1 extends to 8K at 60Hz. DisplayPort 1.4 offers higher bandwidth, supporting 4K at 144Hz or 8K at 60Hz with DSC compression, and DP 2.0 nearly triples this capacity. DisplayPort generally offers more bandwidth for the most demanding surgical imaging.
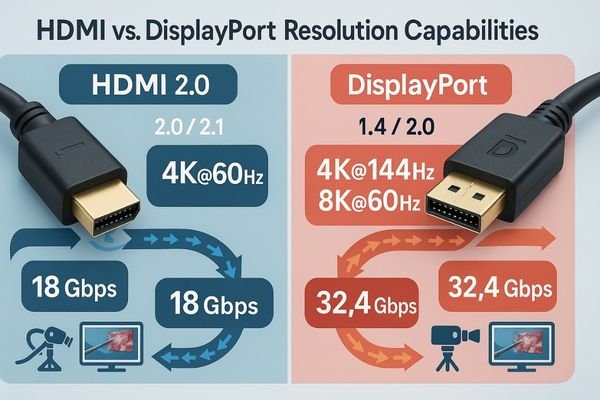
The fundamental difference between HDMI and DisplayPort lies in their bandwidth capabilities. HDMI 2.0, which is still common in many medical facilities, provides up to 18 Gbps of bandwidth. This is sufficient for 4K (3840×2160) resolution at 60Hz with standard color depth, which meets the needs of many endoscopic cameras and surgical imaging systems. However, as we move toward more demanding applications like 3D visualization or fluorescence imaging, this bandwidth becomes a limitation. HDMI 2.14 significantly increases the available bandwidth to 48 Gbps, enabling 8K resolution or 4K with higher refresh rates and deeper color. DisplayPort, on the other hand, has historically offered more bandwidth than equivalent HDMI versions. DisplayPort 1.4 delivers up to 32.4 Gbps, supporting 4K at higher refresh rates or 8K with Display Stream Compression (DSC). The newer DisplayPort 2.05 provides a massive 80 Gbps, making it ready for future imaging technologies. Our MS321PC monitor includes both HDMI 2.0 and DisplayPort 1.4 inputs, giving surgical teams flexibility while supporting the highest-quality 4K signals.
HDMI vs. DisplayPort Bandwidth and Resolution Capabilities
| Interface Standard | Maximum Bandwidth | Maximum Resolution (Uncompressed) | Maximum Resolution (Compressed) | HDR Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 2.0 | 18 Gbps | 4K @ 60Hz (8-bit) | N/A | Limited HDR10 |
| HDMI 2.1 | 48 Gbps | 4K @ 120Hz or 8K @ 60Hz | N/A | Full HDR10, HDR10+, HLG |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | 32.4 Gbps | 4K @ 120Hz | 8K @ 60Hz with DSC | HDR10, HDR10+ |
| DisplayPort 2.0 | 80 Gbps | 8K @ 60Hz or 4K @ 240Hz | 16K @ 60Hz with DSC | HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision |
Is SDI still relevant for high-resolution surgical video transmission?
You question whether to maintain SDI infrastructure in your OR. Surgical towers increasingly offer HDMI outputs, but you wonder if SDI still offers advantages for image transmission reliability.
Yes, SDI remains relevant for surgical video transmission despite bandwidth limitations. While 3G-SDI only supports 1080p, the newer 12G-SDI standard handles 4K at 60Hz over a single cable. SDI offers several advantages over consumer standards: extremely reliable long-distance transmission, robust locking connectors, and native support in many surgical cameras.

Serial Digital Interface (SDI)6 has long been the gold standard for professional video transmission in broadcast and medical environments. Its development has paralleled the evolution of video resolution. Standard SDI (270 Mbps) supported standard definition, HD-SDI (1.5 Gbps) enabled 720p and 1080i, and 3G-SDI (3 Gbps) brought full 1080p capability. For today’s 4K imaging needs, the industry has developed 6G-SDI (6 Gbps) and 12G-SDI7 (12 Gbps). What continues to make SDI valuable in surgical settings is its inherent reliability. SDI uses robust BNC connectors8 that lock firmly in place, eliminating the risk of accidental disconnection. The signal can travel over coaxial cable for distances up to 100 meters without quality degradation, which is particularly important in large hybrid operating rooms. Additionally, SDI is designed for professional environments with strong error correction and minimal latency. Our MS430PC surgical monitor incorporates both 12G-SDI and quad-link 3G-SDI inputs, acknowledging that many hospitals maintain a mix of legacy and cutting-edge [imaging equipment](https://reshinmonitors.com/endoscopic-monitor-1080i-deinterlacing-real-time-1080p/ “imaging equipment”). This ensures compatibility with both existing and future video systems.
What bandwidth limitations affect DVI interfaces in medical displays?
Your facility has older medical devices that only output DVI signals. You worry these connections will prevent you from adopting higher-resolution surgical monitors or will force you to replace functional equipment prematurely.
DVI is significantly bandwidth-limited compared to modern standards. Single-link DVI maxes out at 1920×1200 resolution, while dual-link DVI can reach 2560×1600. Neither can support 4K or higher resolutions, creating a bottleneck for modern surgical imaging. This makes DVI increasingly obsolete for new high-resolution medical displays.

Digital Visual Interface (DVI9) was revolutionary when it appeared in 1999 as one of the first fully digital video standards. However, its bandwidth limitations have become increasingly restrictive as display resolutions have increased. A single-link DVI connection provides only 3.96 Gbps of bandwidth, which caps resolution at 1920×1200 at 60Hz. Dual-link DVI doubles this to about 7.92 Gbps, supporting up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz. For comparison, modern 4K resolution10 at 60Hz requires at least 12.54 Gbps of bandwidth, well beyond DVI’s capabilities. This creates a significant problem in medical facilities, where equipment replacement cycles are longer than in consumer markets. Many perfectly functional older imaging devices are limited to DVI output, yet the monitors they connect to may need replacement. The best solution is a display that provides backward compatibility11 through DVI inputs while offering future-proof connections for newer devices. Our compact MS220S monitor includes DVI-D inputs specifically to support legacy devices while still providing HDMI and DisplayPort for modern sources, ensuring hospitals can transition at their own pace without sacrificing functionality.
Are USB-C and Thunderbolt viable options for 4K surgical monitors?
You wonder if the convenience of USB-C connections seen in consumer technology could simplify cable management in your operating room. A single cable for video, power, and data seems appealing, but you question if it meets medical-grade reliability standards.
Yes, USB-C and Thunderbolt are increasingly viable for surgical monitors. USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode supports 4K at 60Hz, while Thunderbolt 3/4 handles 4K at 120Hz or dual 4K displays. Their advantages include simplified cabling, power delivery, and data transfer through a single connection—though adoption in medical environments is still emerging due to certification requirements.

USB-C12 and Thunderbolt represent the newest generation of video interfaces, offering unprecedented versatility. A standard USB-C port with DisplayPort Alt Mode provides up to 32.4 Gbps of video bandwidth—equivalent to DisplayPort 1.4. This is ample for 4K resolution at 60Hz with full 10-bit color depth, meeting the needs of most current surgical imaging systems. Thunderbolt 3 and 413 raise this capability even further, supporting dual 4K displays or single displays at higher refresh rates. The true innovation of these interfaces lies in their multi-functionality. The same cable that carries video can also: deliver up to 100W of power, transfer data at up to 40 Gbps, transmit audio, and connect peripherals. This could significantly reduce cable clutter in the OR while simplifying connections. For instance, a mobile ultrasound system could connect to a display through a single cable rather than separate power, video, and data connections. The MS275P monitor features USB-C connectivity with power delivery, allowing it to serve as a hub for both imaging and device management. As medical device manufacturers increasingly adopt these standards, their presence in the OR will only grow.
How does Reshin ensure interface flexibility for various high-resolution signals?
You need a surgical monitor that works with all your existing equipment and future acquisitions. The risk of purchasing a display with incompatible connections seems high, potentially wasting valuable resources.
Reshin ensures interface flexibility through a multi-standard approach. Our surgical monitors include HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.4, 12G-SDI, and USB-C inputs on a single device. We also provide intelligent signal detection, scaled output options for secondary displays, and regular firmware updates to support emerging standards.
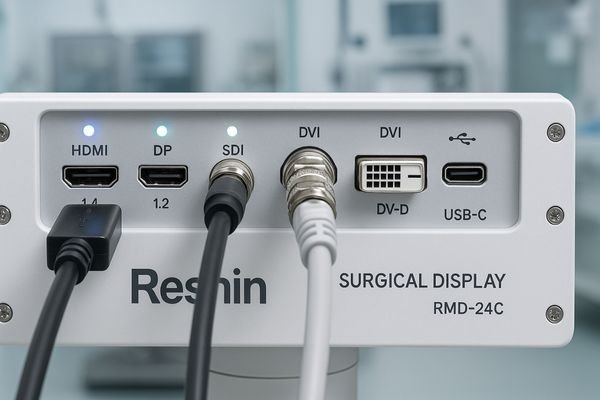
Interface flexibility is a cornerstone of our design philosophy. We understand that operating rooms contain a mix of equipment from different eras and manufacturers, all of which need to communicate seamlessly. Rather than forcing hospitals to standardize on a single interface, we build our monitors to adapt to whatever signals are available. Every Reshin surgical monitor includes multiple interface options to handle a wide range of signal types and resolutions. This includes legacy connections like DVI-D for older equipment, professional standards like 12G-SDI for broadcast-quality video transmission, and the latest HDMI 2.0 and DisplayPort 1.4 ports for maximum resolution and refresh rates. For the most demanding applications, models like our MS321PB also include USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode14, which can carry 4K video while simultaneously charging a connected device and providing USB data connectivity. Beyond physical connections, we employ advanced scaler technology15 that automatically detects the incoming signal format and optimizes the display accordingly. This ensures the best possible image quality regardless of source resolution. Many of our models can also output video to secondary displays, enabling consistent image distribution throughout the operating room.
Surgical Monitor Input Compatibility Matrix
| Signal Source | Resolution | Recommended Interface | Alternate Interface | Cable Length Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4K Endoscopic Camera | 3840×2160 @ 60Hz | HDMI 2.0 | DisplayPort 1.4 | 3-5 meters (HDMI), 3-15 meters (DP) |
| Fluorescence Imaging | 1080p @ 60Hz with 10-bit color | DisplayPort 1.2+ | HDMI 2.0 | 3-15 meters (DP), 3-5 meters (HDMI) |
| Mobile C-Arm | 1080p @ 30Hz | 3G-SDI | HDMI 1.4+ | Up to 100 meters (SDI), 3-5 meters (HDMI) |
| Integration System | 4K @ 60Hz | 12G-SDI or DisplayPort 1.4 | HDMI 2.0 | Up to 100 meters (SDI), 3-15 meters (DP) |
| Legacy Device | 1080p or lower | DVI-D | HDMI 1.4 (with adapter) | Up to 5 meters (DVI), 3-5 meters (HDMI) |
Conclusion
Video interface standards create real resolution limits for surgical displays. Choose monitors with multiple inputs—HDMI 2.0/2.1, DisplayPort 1.4, SDI, and USB-C—to ensure compatibility across all devices while supporting the highest resolutions your procedures require. For surgical displays offering versatile, high-bandwidth connectivity, contact Reshin at martin@reshinmonitors.com.
- Explore how high-resolution imaging enhances surgical precision and outcomes, making it essential in today’s medical practices. ↩
- Discover the impact of 4K resolutions on surgical procedures and patient safety, a must-read for medical professionals. ↩
- Understanding video interfaces is crucial for optimizing image quality in surgeries; learn about the best options available. ↩
- Explore the advancements of HDMI 2.1, including higher bandwidth and support for 8K resolution, which are crucial for modern imaging technologies. ↩
- Learn about DisplayPort 2.0’s impressive 80 Gbps bandwidth and its potential for future imaging technologies, enhancing your understanding of display options. ↩
- Explore this link to understand the significance of SDI in professional video transmission and its applications in various fields. ↩
- Learn about the advantages of 12G-SDI, including its capabilities for high-resolution video and compatibility with existing systems. ↩
- Discover why BNC connectors are essential for reliable video connections, especially in critical environments like surgery. ↩
- Understanding DVI’s limitations can help you appreciate the advancements in display technology and make informed decisions for upgrades. ↩
- Exploring the bandwidth requirements for 4K resolution will give you insights into the capabilities of modern display standards and their importance. ↩
- Learning about backward compatibility can help you understand how to maintain functionality with older devices while upgrading to newer technology. ↩
- Explore how USB-C enhances connectivity and efficiency in medical devices, streamlining operations in healthcare settings. ↩
- Learn about the advanced capabilities of Thunderbolt 3 and 4, which can elevate your video interface experience significantly. ↩
- Discover the advantages of USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode for high-resolution video and data connectivity in medical applications. ↩
- Learn about advanced scaler technology and its role in optimizing display quality for various signal formats in surgical settings. ↩



